Engineering a tissue that achieves a 31.50 g/g liquid capacity while adhering to the 25-minute settling window required for septic safety is a high-stakes technical challenge. Miscalculating this balance does more than trigger immediate clogs; it slashes the actual lifespan of rooftop units (RTUs) by up to 40% and inflates annual maintenance costs through energy inefficiencies and emergency labor premiums.
This analysis dissects the physics of wicking and disintegration, focusing on the ISO 12625-8 basket-immersion protocol and the performance of precision-engineered fibers like Teijin Tenax™. We evaluate how automated testing standards, specifically the TECHLAB WAT model, provide the empirical data necessary to optimize drainage health in marine, RV, and commercial facility environments.
Capillary Action: The Science of How Tissue Absorbs Liquids
Capillary action uses microscopic gaps in cellulose fibers to pull liquids upward against gravity, driven by the molecular forces of adhesion, cohesion, and surface tension.
The Physics of Wicking: Adhesion, Cohesion, and Surface Tension
Paper tissue acts as a network of microscopic conduits rather than a solid mass. Cellulose fibers contain hydroxyl (OH) groups that form immediate hydrogen bonds with water molecules. This chemical attraction initiates the wicking process the moment liquid touches the surface.
Liquid movement through these fiber gaps relies on three specific physical forces:
- Adhesion: Water molecules stick to the cellulose walls of the fiber pores.
- Cohesion: Water molecules cling to each other, creating a continuous liquid column.
- Surface Tension: The liquid surface acts as an elastic membrane, pulling the column upward through the pores.
The porous structure creates a pressure differential. This allows the tissue to transport liquid vertically without the need for external pumps or mechanical force.
Fiber Engineering: Maximizing Absorbency with Virgin Wood Pulp
Tissue engineering replicates the “xylem” structure found in plants. Wood fibers are essentially lignified tubes designed by nature to transport water. Using 100% virgin wood pulp ensures these channels remain open and uncontaminated by the shorter, broken fibers often found in recycled alternatives.
Fiber density and arrangement (GSM) dictate the “capillary radius.” Smaller gaps generate higher suction and faster wicking, but engineers must balance this against the total storage capacity of the sheet. If the pores are too small, the tissue reaches saturation too quickly.
Advanced OEM manufacturing maintains wicking efficiency by excluding specific inhibitors:
- Fluorescent Whiteners: Excess chemicals can coat fibers and block pore openings.
- Synthetic Binders: Hydrophobic resins can seal the cellulose surface, preventing hydrogen bonding.
- Lignin Residue: Proper pulping removes lignin to ensure fibers remain hydrophilic and flexible.
By preserving the purity of the cellulose, the product maintains predictable absorption rates and rapid surface drying, which are critical for hygiene in high-traffic commercial environments.

Absorption Rate (Seconds) vs. Capacity (Grams of Water)
Absorption rate measures wetting speed in seconds; capacity quantifies total water retained in grams per gram (g/g). ISO 12625-8 standards define both to predict infrastructure clog risks.
Kinetics vs. Equilibrium: Understanding Wetting Speed and Saturation Limits
Absorption rate defines wetting kinetics. This is the exact time in seconds a sample takes to reach full saturation. It determines how fast a product manages initial moisture and begins the disintegration process. Capacity measures equilibrium uptake—the maximum liquid weight the fiber structure holds.
Performance metrics shift based on the environment and material composition. High-performance absorbents demonstrate significant variance depending on the liquid type:
- Deionized Water Capacity: 31.50 g/g
- Saline Capacity: 5.25 g/g
- Fiber Physics: Hydroxyl groups and capillary action drive initial uptake.
Rate and capacity do not share a linear relationship. A paper grade designed for instant wetting might saturate quickly but hold less total volume than a slower-absorbing, high-density fiber. Engineers must select materials based on whether the application requires immediate “flash” absorption or long-term retention.
ISO 12625-8 Protocol: Standardized Basket-Immersion and Metric Computation
ISO 12625-8 provides the primary framework for quantifying tissue performance. This standard uses a basket-immersion test to generate repeatable data. Automated systems, like the TECHLAB WAT model, remove manual timing errors to calculate precise averages and standard deviations.
- Sample Parameters: 76 mm width; 5.0 ± 0.2 g mass.
- Immersion Cycle: 30 ± 1 seconds in deionized water.
- Drainage Specs: 60 ± 1 seconds at a 30 ± 3° angle.
- Basket Mass: 3.0 ± 0.1 g metal mesh.
Infrastructure engineers use these data points to prevent system failures. For example, a 5g sample with a 31.50 g/g capacity results in a saturation weight of approximately 157.5g. Knowing this weight allows facilities to assess the risk of pipe clogs and calculate the necessary hydrostatic pressure for waste removal.
Disintegration Speed: The “Mason Jar” Test for Septic Safety
The Mason Jar test mimics septic turbulence to ensure solids settle within 25 minutes. This aligns with 2–45 MPI percolation standards to prevent clogs and groundwater contamination.
| Testing Phase | Energy/Velocity (G-Value) | Duration | Septic Benchmark |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flash Mixing | 200 RPM (G=1,500–4,000) | 20–60 Seconds | High-energy entry simulation |
| Flocculation | 20–30 RPM (G=20–75) | 5 Minutes | Fiber aggregation check |
| Settling | Static | 25 Minutes | Sand-level sedimentation |
Methodology: Simulating Wastewater Turbulence and Sedimentation
Before mechanical disintegration begins, cellulose fibers use capillary action to absorb water. Hydroxyl groups form hydrogen bonds that draw liquid into the porous structure. This saturation prepares the material for the Mason Jar protocol, which uses specific mixing velocities to predict real-world breakdown.
- Flash Mixing Protocol: Tests initial disintegration at 200 RPM to simulate the high-energy impact of wastewater entering a septic tank.
- Flocculation Simulation: Low-speed mixing at 20–30 RPM evaluates if fibers aggregate or remain suspended in the effluent.
- 25-Minute Settling: Particles must settle into distinct layers within this window to prevent turbidity from clogging the drain field pipes.
- Soil Texture Analogy: Uses a 50% soil-to-water ratio to observe how sand (settles in minutes) versus clay (stays suspended) affects fiber movement.
Technical Metrics: Velocity Gradients and Percolation Standards
Engineering benchmarks define septic safety. Velocity gradients, or G-values, quantify the mixing energy required for total fiber dispersion. If the material fails to settle properly during these tests, it risks violating regional drainage regulations.
- Velocity Gradients: Rapid mix targets G=1,500–4,000 /sec for dispersion, while flocculation requires G=20–75 /sec.
- Percolation Rates: Standard drain fields require infiltration speeds of 2 to 45 minutes per inch (MPI) to protect groundwater.
- Plastic Limit Verification: Soil threads rolled to 1/8 inch diameter confirm if the moisture level allows for mechanical disintegration.
- Settlement Efficiency: Sand-heavy drainage settles in minutes, whereas clay-heavy environments keep fibers suspended, increasing backup risks.
Scale Your Brand with Global Toilet Paper OEM Experts

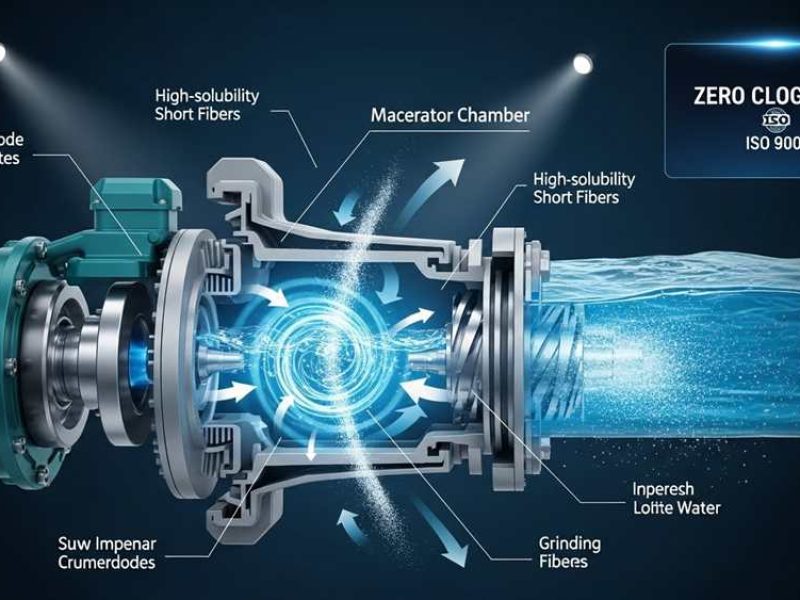
Fiber Selection for High-Solubility: Why Short Fibers Win
Short 2–12mm fibers prevent physical entanglement and clogs. Fine deniers combined with 10% moisture ensure uniform dispersion and rapid breakdown in plumbing systems.
| Fiber Type | Fineness (dtex) | Length (mm) | Solubility / Feed Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET Ultra-Short | 0.83 – 6.66 | 2 – 12 | 0mg/100g parallel stuck fibers |
| Teijin Tenax™ | N/A | 3 – 25 | 3.14% CV (Feed Stability) |
| Short-cut Bamboo | 1.10 – 2.00 | Short-cut | High strength-to-weight ratio |
| Grass Fibers | 0.83 – 1.64 | Short-cut | Faster disintegration than wood pulp |
The Physics of Dispersion: Why Length and Surface Tension Matter
Ultra-short fibers ranging from 2mm to 12mm eliminate the “stuck fiber” effect. While standard 25mm textile fibers aggregate in parallel and cause immediate blockages, these shorter geometries remain isolated. They bypass the physical entanglement that typically ruins plumbing infrastructure.
Dispersants create electrostatic repulsion between individual strands. At a concentration of 10g per 1m³ of water, these fibers yield zero parallel sticking or dyed spots. Fibrillated HDPE and PET variants provide the necessary shear resistance to stabilize slurry rheology without the swelling that triggers clogs.
Moisture control acts as the primary catalyst for solubility. Maintaining moisture at approximately 10% prevents sedimentation in aqueous media. This specific level ensures the fiber remains stable during production but breaks down rapidly once it hits the waste stream.
Technical Performance Benchmarks: Denier, Feedability, and Strength
High-solubility PET fibers utilize fineness specifications between 0.83dtex and 6.66dtex, translating to diameters of 9μm to 25μm. This fineness allows for a denser fiber count without increasing the physical bulk that prevents disintegration.
Industrial feedability data confirms that precision-cut fibers minimize manufacturing clogs. Chopped fibers like Teijin Tenax achieve a Coefficient of Variation (CV) of 3.14%. In contrast, lower-grade competitors often show a 12.68% CV, which leads to inconsistent fiber loading and mechanical downtime.
- Natural Fiber Comparison: Bamboo (1.10-2.00dtex) and grass fibers (0.83-1.64dtex) offer high strength-to-weight ratios while disintegrating faster than traditional wood pulp.
- Tensile Performance: Advanced PET variants maintain high tensile strength and low elongation at break, keeping the product durable when dry.
- Loading Capacity: Formulations typically support 10-50% fiber loading by weight without sacrificing flow properties.
These material selections ensure the paper or composite remains structurally sound during use but loses all integrity when submerged. This balance is critical for high-solubility applications where infrastructure protection is a priority.
Testing for Marine and RV Applications: The Gold Standard
Rapid disintegration is the priority. 100% virgin wood pulp ensures tissues dissolve fast enough to clear macerator pumps and protect holding tank sensors in compact systems.
The Mechanics of Rapid Dissolution in Compact Waste Systems
Marine vessels and RVs use macerator pumps and vacuum flush technology rather than gravity-fed drains. These systems require fibers to break down immediately upon hitting the water to prevent mechanical failure.
Manufacturers use 100% virgin wood pulp to achieve this. Recycled fibers often contain binding agents that resist water penetration, causing the paper to remain intact and clog narrow pipework.
High solubility also prevents “pyramiding” in holding tanks. When tissue dissolves completely, it cannot accumulate and foul electronic tank-level sensors, which is a common cause of system downtime in mobile applications.
Standardized Testing Protocols and Compliance Requirements
Testing protocols ensure that every batch of specialized tissue performs predictably in high-pressure or low-volume flush cycles. Reliability in these environments depends on strict adherence to technical benchmarks.
- ISO 9001: Certified manufacturing processes maintain consistent GSM (grams per square meter) and ply-bond strength.
- Disintegration Timing: Laboratory tests measure the exact seconds required for 2-ply to 5-ply tissues to lose structural integrity under agitation.
- Chemical Safety: Compliance with FDA and EU regulations ensures the paper composition will not disrupt the bacteria in onboard biological treatment systems.
By meeting these standards, suppliers ensure that tissue products support the longevity of expensive macerator and sensor components in marine and RV environments.

The ROI of Clog-Prevention for Large Facilities
Proactive maintenance extends HVAC lifespans from four to nine years, slashes energy overhead by 50%, and reduces labor costs by 15% through adherence to hydraulic design standards.
Capital Expenditure Protection: Asset Lifespan and Risk Mitigation
Facility managers often treat drainage as a background concern until a backup occurs. This reactive stance forces equipment to fail decades before its design life ends, wasting capital on premature replacements.
- HVAC Compressors: 9-year lifespan (preventive) vs. 4 years (reactive).
- Rooftop Units (RTUs): 20-year design potential vs. 12-year actual failure (40% loss).
- Emergency Costs: Proactive cleaning avoids repair premiums and productivity downtime in high-traffic zones.
Investing in scheduled drain line cleaning stops the cascading failures that lead to water damage. Keeping clean-outs accessible and functional ensures long-term infrastructure health rather than constant crisis management.
Operational Efficiency: Energy Savings and Maintenance Frequency
Efficiency drops when systems fight blockages. Adhering to the HEC-22 Urban Drainage Design Manual ensures that inlets maintain high hydraulic efficiency and low clogging potential during peak discharge.
- Energy Cost Inflation: Annual costs rise from $3,000 to $4,500+ per unit due to clogged coils.
- Maintenance Savings: 15% reduction in costs by using high-solubility paper products.
- Inspection Cadence: Quarterly camera scoping for high-traffic sites; bi-annual for standard commercial buildings.
Switching to high-capacity jumbo rolls and paper with high solubility reduces plumbing stress. These choices prevent backups and ensure the facility stays compliant with NFPA and MEP engineering standards.
Final Thoughts
Absorbency is a liability if it triggers infrastructure failure. Prioritize 100% virgin wood pulp and short fibers to protect high-traffic plumbing without sacrificing user hygiene.
Audit your stock with a 25-minute “Mason Jar” test immediately. Switch to high-solubility paper to slash maintenance labor by 15% and prevent premature equipment replacement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is absorbency a critical factor in determining toilet paper value?
Absorbency dictates cost-efficiency. High-bulk, open fiber structures following ISO 12625-8 standards remove moisture with fewer sheets. This reduces total waste and prevents excess paper mass from triggering plumbing clogs.
How can I verify if toilet paper is truly safe for septic tanks?
Use the “Mason Jar Test.” Shake several sheets in a jar half-filled with water; septic-safe paper must break down almost immediately. A follow-up settle test ensures fragments sink to the bottom quickly, indicating they won’t obstruct septic flow.
Does bamboo toilet paper dissolve faster than traditional wood pulp paper?
Technical data shows bamboo often dissolves slower. Due to a higher burst index (1.32-2.36 kPa.m²/g) and superior tensile strength, bamboo-based tissues exhibit lower disintegration rates than high-solubility wood pulp.
What is the global standard for testing tissue disintegration speed?
The international benchmark is EN ISO 12625-17:2021. This protocol measures tissue breakdown in water after specific agitation intervals of 30 seconds, 2 minutes, and 10 minutes to verify drainage system safety.
Can absorption be increased without making the paper thicker or heavier?
Yes. Manufacturers cross-link bleached eucalyptus kraft pulp (BEKP) with N,N’-methylenebisacrylamide (MBA) at 0.2-0.5g per gram of polymer. This achieves a water absorption capacity of 11.8 g/g in lightweight 20 g/m² sheets without adding bulk.
What are the risks of using high-wet-strength paper in older facilities?
High-wet-strength paper retains 20-35% of its dry tensile strength when wet, whereas standard paper retains only 3-10%. In aging buildings, these resilient fragments persist in the pipes, significantly increasing the risk of clogs and drainage failure.