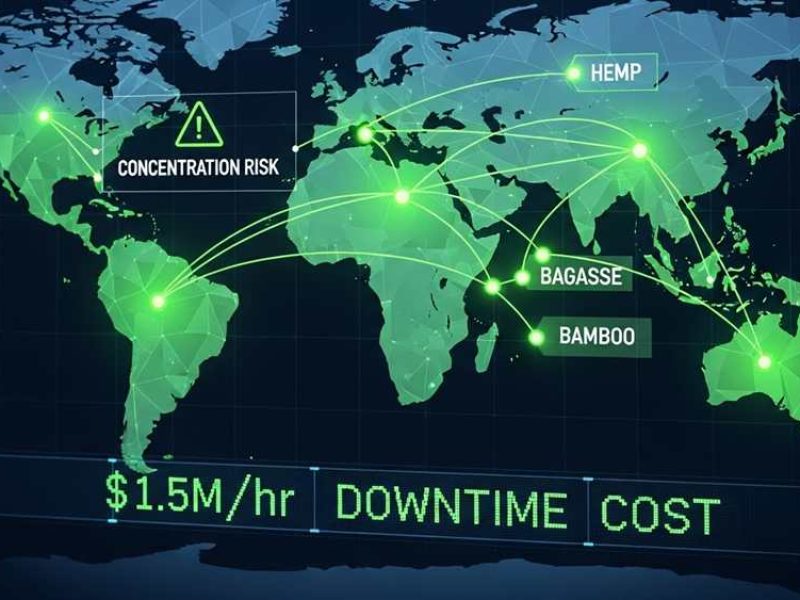
Supply chain over-concentration transforms regional logistics bottlenecks into total production halts, with downtime costs in critical fiber sectors exceeding $1.5 million per hour. Integrating alternative fibers like hemp and sugarcane bagasse mitigates these single-source vulnerabilities while leveraging materials that offer up to 920 MPa in tensile strength—nearly double the mechanical resistance of conventional cotton benchmarks.
This analysis evaluates the mechanical integrity and processing requirements of non-wood feedstocks, focusing on ASTM D6400 compostability for bagasse and the HempTrain™ decortication system for high-yield fiber output. We examine the technical hurdles of silicate management in wheat straw and the manufacturing protocols required to maintain ISO 9001 and FDA hygiene standards across a 2,860-ton monthly production capacity.
Why Fiber Diversification is Essential for Supply Chain Stability
Sourcing alternative fibers like hemp or bagasse prevents $1.5M/hour downtime losses and supplier lock-in while boosting market competition and consumer surplus by 35%.
Mitigating Operational Risks and Single-Source Vulnerabilities
Supply chain failures stem from over-concentration. Relying on one vendor or geographic zone turns a regional crisis into a total production halt. Diversifying into hemp and agricultural by-products builds resilience against these market failures.
About 78% of infrastructure faults affect only a single source. A distributed supply chain lets you pivot without stopping production. This strategy breaks the “supplier lock-in” that gives dominant vendors excessive leverage during regional shortages or logistical bottlenecks.
Quantifying the Economic Value of Sourcing Diversity
Financial risks are high. In sectors like undersea fiber-optics, downtime costs exceed $1.5 million per hour. Diversity mitigates these losses and generates market value through increased competition and reduced single-point failure risks.
- Market Surplus: Supplier diversity accounts for 25% of total surplus and 35% of consumer surplus in highly competitive markets.
- Scale Investment: Critical resilience programs often require initial investments of £250 million to establish high-risk vendor independence.
- Innovation Metrics: New material entry drives improvements in GSM and ply-strength while lowering long-term price points.
Investing in regional processing reduces reliance on volatile international shipping routes. Spreading sourcing across different continents ensures operational capabilities remain flexible regardless of localized trade disruptions or natural disasters.
Hemp Fiber: The Resilience Powerhouse
Hemp’s high-cellulose bast structure delivers 920 MPa tensile strength and exceptional dimensional stability, making it significantly stronger and more durable than cotton or synthetic alternatives.
Structural Anatomy and Mechanical Integrity
Hemp fiber relies on a complex bast structure to maintain its mechanical integrity. The plant’s secondary walls contain long cellulose microfibrils that provide the primary load-bearing capacity for industrial applications. Lignin and hemicellulose networks shield these fibers from environmental rot and mechanical degradation.
- Microfibril Diameter: 10–30 nm
- Microfibril Angle: 2–6.2°
- Tensile Strength: 390 to 920 MPa
- Young’s Modulus: 35 to 96 GPa
- Elongation at Break: 1.6–1.7%
The low elongation rate ensures the material remains dimensionally stable under stress. This stability makes hemp two to three times stronger than cotton in textile and rope configurations. High stiffness profiles allow hemp to replace fiberglass in various composite reinforcements.
Technical Metrics and Emerging Industry Standards
Engineers now utilize quantitative physics-based metrics instead of subjective grading. These measurable specifications allow hemp to compete directly with technical textiles and synthetic insulation materials. Standardized testing protocols ensure consistency across different harvests and cultivars.
- Technical Length: 1000–3000 mm
- Elementary Diameter: 10–51 μm
- Fiber Density: 1.48–1.52 g/cm³
- Tenacity: 47–80 cN/tex
- HempWool Density: 35 kg/m³ (validated via ASTM C209)
- Testing Standards: ASTM WK75916 and NIFA optical fiber analysis
Adopting these standards mitigates the risks associated with single-source supply chain failures. Diversifying sourcing through domestic capacity and transparent benchmarks provides a safety net against the high-cost disruptions common in concentrated fiber markets. Modern decortication methods now achieve 61.8% to 67.5% efficiency for hackled fibers, supporting large-scale industrial pivots.

Sugarcane Bagasse: Utilizing Agricultural By-products
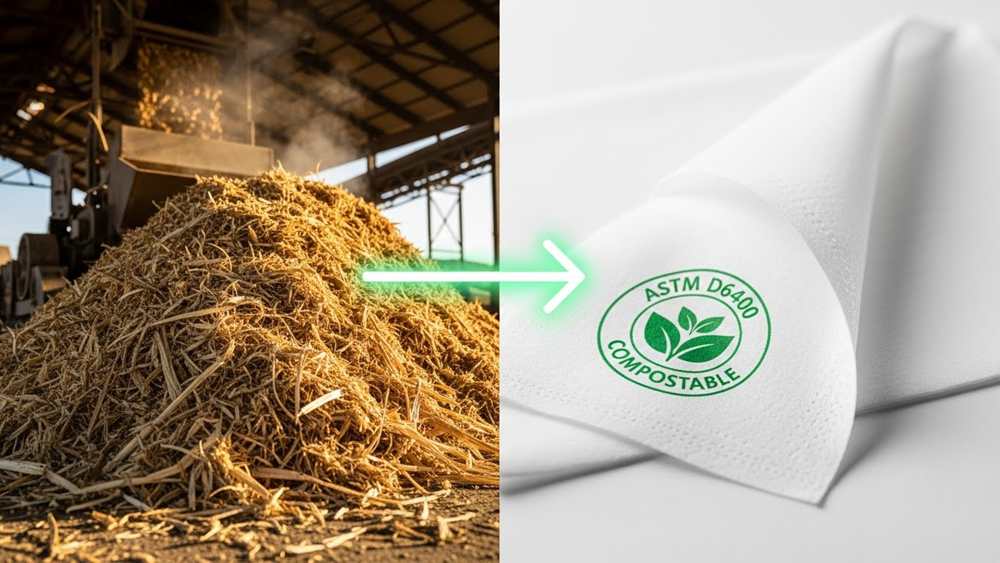
Sugarcane bagasse provides 40-50% cellulose for high-performance tissue manufacturing, biodegrading fully within 60 days to meet ASTM D6400 compostability standards.
Bagasse is the fibrous residue remaining after sugar millers crush cane. It serves as a viable, non-wood alternative to virgin pulp because its chemical composition mirrors the structural requirements of industrial tissue and hygiene products.
Structural Composition and Biodegradability Standards
The material’s durability comes from its dense cellulose framework. Unlike some agricultural residues that lack the “snap” of wood fiber, bagasse maintains mechanical strength throughout the manufacturing process.
- Cellulose Content: 40-50% (provides primary structural framework).
- Hemicellulose and Lignin: Each accounts for 25% of the mass, aiding in fiber bonding.
- ASTM D6400 Certification: Fully composts into nutrient-rich soil within 60 days.
- Waste Upcycling: Replaces virgin wood pulp by utilizing residues often burned at sugar mills.
Technical Performance and Material Processing Data
Manufacturers must control particle size to ensure uniform yields during thermochemical conversion. Standardized density models allow for predictable scaling in industrial-sized manufacturing facilities.
- Proximate Profile: 76.02% volatile matter and 10.56% ash on a dry basis.
- Optimal Particle Size: 1.0-3.55 mm ensures high yields and material uniformity.
- Validation Standards: Real density via ASTM D4892-84 and bulk density via ASTM E873-82.
- Elemental Analysis: Low sulfur (0.05%) and nitrogen (0.36%) emissions during processing.
This material handles thermal degradation effectively, peaking between 310-330°C. Using bagasse reduces reliance on single-source timber chains while meeting rigid environmental and structural performance benchmarks.
Build Your Premium Toilet Paper Brand with 30 Years of OEM Expertise

Wheat Straw Tissue: The Challenges of Silicates and Softness
High silica (4.8–7.0%) and fines (35–47%) degrade tissue softness and damage equipment. Success requires alkaline pulping for silicate removal and enzyme treatments to optimize fiber texture.
Silicate Management: Mitigation Strategies for High Ash Content
Wheat straw’s high silica levels create immediate production friction. These silicates accumulate on Yankee dryer coatings, causing abrasive equipment wear and increasing dust levels during high-speed tissue manufacturing.
- Silica Content: 4.8–7.0% by mass (up to 76% of total ash)
- Cellulose Levels: 47.7% (significantly lower than wood pulp)
- Removal Rate: 77–90% via 16% sodium carbonate alkaline pulping
- Ash Range: 6.3–10.5% in raw samples
Standard mechanical treatments cannot handle this mineral load. Producers use alkaline pulping to drop ash levels and protect machinery from the buildup that typically ruins softwood-optimized lines.
Enhancing Softness: Managing Fines and Enzyme Pretreatment
Wheat straw generates a massive volume of fines compared to hardwood alternatives like Eucalyptus. While these fines increase refining response, they also kill sheet strength and tactile softness if left unmanaged.
- Fines Generation: 35–47% volume
- Average Fiber Length: 0.806 mm post-treatment
- Primary Enzymes: Lipase and xylanase
- Structural Focus: Hemicellulose degradation and surface lipid removal
Enzyme pretreatment solves the texture gap. By removing surface lipids and boosting fiber swelling, mills achieve a soft, consumer-grade finish without the structural collapse typically associated with high-fines non-wood pulp.

Blended Fibers: Creating the “Hybrid Roll” of the Future
Hybrid rolls blend wood pulp with alternative fibers to maximize tensile strength and stabilize supply chains against million-dollar-per-hour downtime risks.
| Fiber Combination | Mechanical Advantage | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Pulp + Hemp | Enhanced Tensile Strength | High-Traffic Commercial Jumbo Rolls |
| Polyester + Cotton | Reduced Shrinkage & Wrinkles | Hospitality-Grade Facial Tissues |
| Glass Fiber + Natural | High Tear Resistance | Industrial Cleaning Wipes |
Synergistic Blending: The Mechanics of Hybrid Fiber Integration
Engineers create “Hybrid Rolls” by filling structural gaps in the paper web with fibers of varying diameters. This method increases the composite’s density without sacrificing the tactile softness end-users expect. By integrating synthetic and natural components, manufacturers control material behavior during the drying phase.
The process allows for precise adjustment of Grams per Square Meter (GSM) across different ply configurations. Manufacturers utilize these blends to meet specific brand performance requirements while maintaining a balance between durability and comfort.
- Fiber Variations: Hemp, cotton, and glass fibers fill gaps in wood pulp structures.
- Ply Configurations: 2-ply to 5-ply options for customized strength.
- Structural Integrity: Blending reduces common issues like material shrinkage and surface wrinkles.
Performance Metrics and Industrial Application Standards
Industrial fiber diversification acts as a hedge against market volatility. Data from parallel infrastructure sectors shows that disruptions cost over $1.5 million per hour. By diversifying raw material inputs, paper manufacturers mitigate these risks and ensure a consistent monthly production capacity of 2,860 tons.
Regulatory compliance remains a baseline for hybrid production. Factories operate under strict protocols to meet international hygiene and safety requirements for global distribution. This ensures that every roll, whether for hospitality or industrial use, meets consistent quality benchmarks.
- Monthly Capacity: 2,860 tons of consistent hybrid fiber output.
- Compliance Standards: ISO 9001 and FDA hygiene certifications.
- Economic Impact: Diversified sourcing accounts for a 35% increase in consumer surplus by preventing supply lock-in.
- Utility Metrics: Improved “stretch” and “ease of care” for high-traffic environments.

Scalability and Manufacturing Challenges in Alternative Fibers
Mass-market adoption of hemp and bagasse fails at high speeds due to narrow 15°C thermal windows, hydrophilic bonding issues, and precise 1.5 MPa compaction requirements.
| Manufacturing Parameter | Optimal Value/Range | Risk of Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Die Temperature (Hemp) | 177°C (350°F) | Thermal degradation >185°C |
| Pultrusion Pull Speed | 2.03 cm/s (48–60 in/min) | Inconsistent mechanical density |
| Compaction Pressure | ≥1.5 MPa | Poor material impregnation |
| Thermal Window | 170°C – 185°C | Viscosity spikes or fiber damage |
Thermal Degradation and Processing Parameters
High-speed production of alternative fibers hinges on a 15-degree margin. If temperatures drop below 170°C, resin viscosity spikes and stalls the impregnation of the fiber matrix. Push past 185°C, and the molecular integrity of hemp or recycled PLA collapses, reducing the bending modulus of the finished part.
- Target Die Temperature: 177°C (350°F) specifically for hemp pultrusion.
- Processing Floor: 170°C minimum to ensure resin flow.
- Degradation Ceiling: 185°C for recycled polymers (rPLA).
- Compaction Standard: 1.5 MPa minimum for organo sheet hot pressing.
Material Stability and Machinery Adaptation
Natural fibers are inherently hydrophilic. This moisture absorption causes poor dimensional stability and weak interfacial bonding with polymer matrices. Scaling requires moving beyond raw fibers to chemically treated or hybridized versions to prevent matrix yield and fiber micro-buckling under load.
- Throughput Speed: 2.03 cm/s (48–60 in/min) for industrial scalability.
- Fiber Volume Fraction: 37–49% for sheets; up to 70% for pultruded rods.
- Chemical Treatments: Silane, acetylation, or maleate coupling to improve durability.
- Mechanical Peak: 890 MPa flexural strength (Jute) achievable only with proper bonding.
Adapting existing glass-fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP) machinery isn’t a “plug-and-play” process. Operators must recalibrate pulling speeds and cooling rates to accommodate the lower thermal stability of plant matter. Without these custom process validations, alternative fibers remain a niche laboratory interest rather than a viable industrial feedstock.
Final Thoughts
Alternative fiber production demands punishingly narrow 15°C thermal windows and significant capital. However, sticking to single-source timber guarantees catastrophic losses when supply chains inevitably fracture.
Implement “Hybrid Rolls” today to hedge against volatility while maintaining softness. Audit your machinery’s compaction pressure and order a trial batch of hemp-blended pulp to validate your manufacturing floor.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can toilet paper be effectively manufactured from hemp or sugarcane?
Yes. Manufacturers process hemp and sugarcane bagasse using standard pulping and drying methods. Hemp yields 55%-77% cellulose, significantly outperforming wood pulp’s 40%-45%. Consequently, one acre of hemp produces as much pulp as four acres of trees.
What are the primary pros and cons of wheat straw paper products?
Wheat straw reduces the ecological footprint by 20% and repurposes agricultural waste. But it faces challenges with fiber continuity and pesticide residues. High silicate content also makes it difficult to achieve the same softness as virgin wood fibers.
Why are B2B sectors increasingly adopting alternative fibers like hemp?
Superior mechanical performance and ESG compliance drive B2B adoption. Hemp fibers deliver a tensile strength of 500–900 MPa, nearly double that of cotton. This high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for industrial applications and sustainable branding.
Is hemp toilet paper softer than bamboo or traditional wood pulp?
Bamboo is generally softer than hemp. Hemp fibers are naturally stronger and more durable, which creates a slightly coarser texture. Wood pulp remains the softest due to heavy chemical bleaching, but hemp offers better durability and structural integrity.
How does the cost of alternative fibers compare to traditional wood pulp?
Molded fiber pulp is cheap at $50–$150 per ton. However, finished bamboo and hemp paper products typically cost more than wood pulp. Immature supply chains and high specialized processing costs keep these premium alternative prices elevated.
Will alternative fibers work in standard manufacturing machines?
Standard machines require modifications to handle these fibers. You must use compatibilizers like PE-g-MA at 10% of fiber content to maintain tensile resistance. Specialized harvesting and decortication equipment, such as the HempTrain™ system, are necessary for raw material processing.