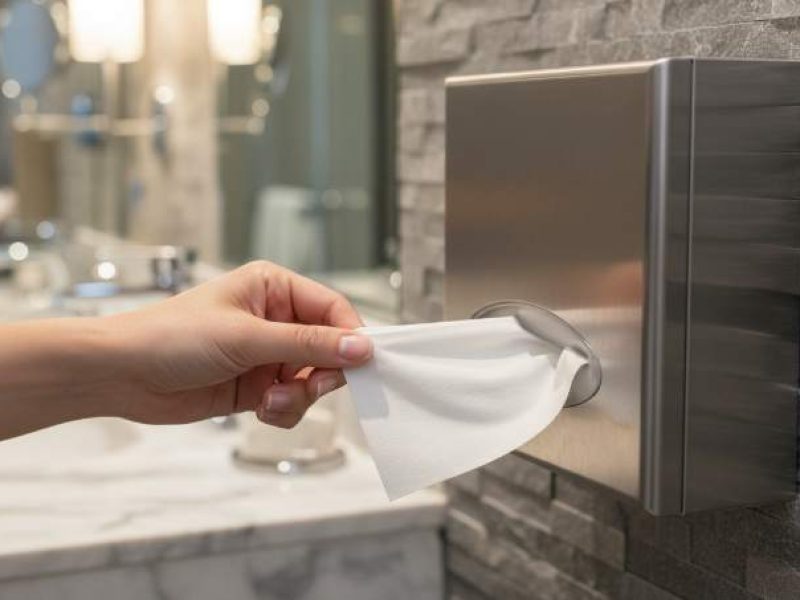
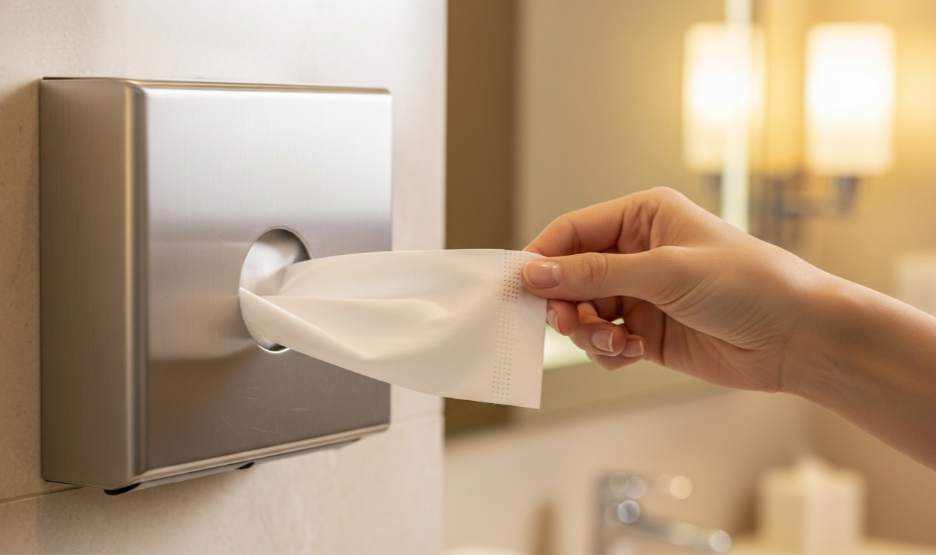
Interfolded (Pop-Up) Tissue reduces cross-contamination from shared-roll handling and directly lowers the risk of failed hygiene audits, guest complaints, and costly compliance fines that can hit occupancy and revenue.
This guide functions as a technical SOP for procurement and facilities teams: it lays out the one-sheet-at-a-time dispensing science that anchors hygienic restroom solutions (the core section), tests claims about whether interfolded systems can cut consumption by roughly 30%, compares V-fold and Z-fold engineering and dispenser mechanics, quantifies unit-cost versus labor-savings, and covers dispenser aesthetics for luxury branding. Use these sections to build spec-ready metrics, on-property testing protocols, and procurement arguments that operations and finance will accept.
Why Is Interfolded Tissue Replacing Rolls in Luxury Hotel Restrooms?
One-at-a-time interfolded dispensers cut material waste, improve hygiene, and shorten housekeeping intervals, delivering measurable operational savings and stronger sustainability credentials.
Single-sheet consumption metrics and how to measure waste reduction
Start with a clear baseline: count rolls used per occupied-room-night for 30–90 days before you switch formats. Use the hospitality waste benchmark—mandatory roll-replacement practices can discard up to 50% of purchased paper—as your reference for upside. After deployment, track sheets dispensed per occupied-room-night and compare against the baseline to quantify material savings and calculate the direct reduction in kilograms or square meters of paper consumed.
Design the pilot to produce actionable data: select interfolded paper grade to match guest expectations (2–5 ply; 13–22 g/m² per ply), assign 10–20% of rooms to the pilot group for a fixed period, and record sheets dispensed, cost-per-meter, and refill frequency. Use those figures to calculate dispenser payback and project annualized savings across the portfolio.
- Baseline window: 30–90 days of rolls-per-occupied-room-night data.
- Pilot size: 10–20% of rooms; fixed test period (30–90 days recommended).
- Paper spec to match tactile target: 2–5 ply; 13–22 g/m² per ply.
- Compare: pre-deployment rolls used vs. post-deployment sheets dispensed per occupied-room-night.
- Record refill frequency and cost-per-meter to compute dispenser capex payback.
Dispenser specifications, compatibility checks, and installation requirements
Verify physical compatibility before you buy: match dispenser sheet format and dimensions to supplier refills, targeting common widths in the 102–132 mm range where applicable. Confirm dispenser capacity (sheets per refill) and refill weight so housekeeping can plan cycles and storage footprint. Choose lockable, tamper-resistant units with one-at-a-time mechanical or sensor feeds to eliminate double pulls and limit access.
Plan installation and logistics alongside facility teams: confirm mounting plate type, wall clearance, and service access; update housekeeping SOPs to include refill and sanitation intervals; and size bulk storage using existing packaging formats (individual wrap or boxed interfold refills). For large orders, coordinate container-loading parameters—Top Source payloads optimize 40HQ shipments—to minimize landed cost and storage handling.
- Dimension check: ensure dispenser accepts 102–132 mm width refills and stated sheet length.
- Capacity check: confirm sheets per refill and refill weight to plan housekeeping intervals and storage.
- Security: specify lockable, tamper-resistant housings with one-at-a-time feed (mechanical or sensor).
- Installation: verify mounting plate, wall clearance, and service access before ordering mounting hardware.
- Logistics: match refill packaging (individual wrap or boxed) to your storage footprint and 40HQ container planning.
Material choice, hygiene outcomes, and calculating operational ROI
Select material to balance guest experience and sustainability. Use 100% Virgin Wood Pulp for premium softness and tensile strength or choose recycled blends when sustainability targets dominate. Require OBA-free certification and rapid disintegration to protect plumbing. Specify CNC or point-to-point embossing to raise absorbency—manufacturers report roughly 30% improvement—and enforce batch color consistency to avoid visible quality variance in guest rooms.
Quantify ROI with a simple operating model: total cost = (paper spend + waste disposal + housekeeping time) before and after deployment, then add dispenser capex and projected refill frequency to estimate months-to-payback. Monitor hygiene outcomes during the pilot—one-at-a-time access reduces surface contact points and lowers cross-contamination risk—and capture guest feedback and housekeeping time-savings. If pilot metrics meet thresholds, scale with supplier-specified grades and require pre-shipment visual verification to protect quality at volume.
- Material spec: 100% Virgin Wood Pulp or validated recycled blend; OBA-free; septic-safe rapid disintegration.
- Quality controls: CNC/point-to-point embossing (~30% absorbency gain) and batch color consistency checks.
- Hygiene outcome: one-at-a-time dispensing reduces touch points and cross-contamination versus exposed rolls.
- ROI formula: months-to-payback = dispenser capex ÷ (annual paper + disposal + labor savings from reduced refill frequency).
- Scale checklist: validate guest feedback, quantify housekeeping time savings, and require pre-shipment photos/videos for quality assurance.

The Hygiene Advantage: One-Sheet-at-a-Time Dispensing Science
One-sheet dispensing cuts use and contamination by enforcing single-piece pulls, lowering material cost and infection risk across high-turnover facilities.
Pre-installation material specification checklist for one-sheet systems
Specify material and sheet construction that meet luxury feel, plumbing safety, and dispenser mechanics before ordering. Choose 100% Virgin Wood Pulp for premium softness and tensile strength, or select Bamboo or Recycled Pulp only when the sustainability program demands it. Control ply GSM at 13–22 g/m² per ply to balance softness and wet strength; target 2–5 plies depending on guest comfort targets and cost constraints. Require natural brightness of 85–92% and an OBA-free formulation to avoid skin irritation and meet FDA/EU hygiene expectations.
Specify embossing, disintegration, and packaging to match dispenser behavior and plumbing regulations. Ask for CNC point-to-point emboss patterns to increase absorbency roughly 30% compared with flat sheets. Require septic-safe engineering that passes North American and EU rapid-disintegration tests. Confirm interfolded or pop-up stack format and check stack height, edge alignment tolerances, and visible lot markings for batch traceability on every carton.
- Core material: 100% Virgin Wood Pulp (or Bamboo/Recycled when specified).
- Ply & GSM: 2–5 plies; 13–22 g/m² per ply.
- Brightness & chemistry: 85–92% natural brightness; OBA-free.
- Embossing: CNC point-to-point pattern; verify ~30% absorbency improvement.
- Septic/disintegration: certify to North American and EU septic standards; request bench-test reports.
- Package format: interfolded or converted pop-up stacks; verify stack height and edge alignment tolerances with vendor.
- Batch traceability: print lot number and batch color sample on each carton; require pre-shipment visual check.
Dispenser mechanical compatibility and selection criteria
Match tissue geometry to dispenser throat and separation mechanics. Specify sheet widths between 102 mm and 132 mm or order a custom width to fit hardware. Confirm lead-edge orientation and single-sheet separation design so the dispenser prevents double-feeds. Require vendor data for cycles per minute, mean time between jams, and expected double-feed rate per 10,000 dispenses to evaluate throughput and reliability against operational needs.
Design mounting and serviceability into the selection. Specify a wall-mount bracket load rating, lock type, and vandal-resistant fasteners for high-traffic locations. Prefer touch-minimized or pop-up face-plate designs to reduce surface contact and select units with front-loading access and replaceable spring/tension elements to speed housekeeping tasks.
- Sheet width: 102–132 mm standard; confirm custom fit where needed.
- Feed geometry: verify lead-edge orientation, stack capacity, and anti-double-feed separator design.
- Throughput metrics: request cycles/minute, MTBJ (mean time between jams), and double-feed rate per 10,000 dispenses.
- Mounting & security: specify bracket load rating, lock style, and vandal-resistant fasteners.
- Hygiene features: choose touch-minimized or pop-up face-plates.
- Serviceability: require front-loading access and modular spring/tension parts.
Installation and initial commissioning procedure
Survey the site and prepare mounting points before you order. Measure the wall plane, confirm substrate type, and document dispenser height and clearance per the restroom layout to avoid rework. At delivery, verify carton lot numbers, inspect for water damage, and confirm sheet edge alignment before loading to prevent early failures.
Mount units level, torque anchors to vendor specs, and verify lock engagement. Load interfolded stacks one at a time, align the center lead-edge, and set tension per the dispenser manual; do not overfill. Run an initial functional test of 50 pulls across multiple users, log double-feeds or misfeeds, and adjust tension or feed geometry. Record dispenser ID, tissue SKU, batch number, installation date, and commissioning test results in the asset log.
- Site survey: measure wall plane, substrate, mounting height, and clearance.
- Pre-install: verify lot numbers, inspect cartons for water damage, confirm sheet edge alignment.
- Mounting: level dispenser, torque anchors to spec, confirm lock engagement.
- Loading: add interfold stacks one at a time, align center lead-edge, set tension per manual; do not overfill.
- Functional test: perform 50 pulls across multiple users; record anomalies and adjust settings.
- Commission log: dispenser ID, tissue SKU, batch number, installation date, test results.
Operational protocols for housekeeping, replenishment, and waste control
Set clear SOPs for replacements and monitoring to lock in savings. Require staff to replace stacks only when empty and to sign off with replacement time and batch number to maintain traceability. Run a 14–30 day baseline to measure sheets-per-room-night before switching formats; use that baseline to quantify savings and set realistic targets.
Plan inventory by converting historical roll tons into interfold stack units and optimize 40HQ container loads to match MOQ strategy. Train staff on correct loading technique, jam clearing, and infection-control handling (gloves and hand hygiene). Quarantine wet or visibly contaminated packs, record incidents for supplier claims, and track waste-reduction progress—one-sheet systems can aim for up to 50% reduction in discarded partial-roll waste versus mandatory roll replacement policies.
- Housekeeping SOP: replace only empty stacks; sign off with time and batch number.
- Baseline consumption: measure sheets-per-room-night over 14–30 days before changeover.
- Waste target: aim for up to 50% reduction in discarded partial-roll waste compared with roll policies.
- Inventory planning: convert roll tons to interfold stack units; plan 40HQ loads to match MOQ.
- Training: loading technique, jam clearing, and infection-control handling (PPE, hand hygiene).
- Damage handling: quarantine wet/contaminated packs and log incidents for supplier claims.
Verification, performance testing, and KPI monitoring
Run a 30-day pilot and capture dispensing reliability metrics: log double-feed rate, jam incidents, and feed failures per 10,000 dispenses. Measure guest comfort and absorbency through tactile panels and guest sampling on selected plies; collect qualitative scores and compare to target thresholds. Perform septic/disintegration bench tests and confirm results meet North American and EU standards before full roll-out.
Track operational KPIs continuously: sheets per guest-night, cost per sheet, refill time per room, and percentage reduction in discarded material. Set acceptance criteria up front—define a maximum allowable double-feed rate and a minimum guest comfort score—and enforce ongoing quality controls such as regular carton inspections, batch color audits, and mandatory pre-shipment photos or videos from the supplier.
- Reliability tests: log double-feed rate, jam incidents, feed failures per 10,000 dispenses during 30-day pilot.
- Comfort checks: run tactile panels and guest sampling; record qualitative scores by ply.
- Plumbing compatibility: perform septic/disintegration bench tests to NA and EU standards and document passes.
- Operational KPIs: sheets per guest-night, cost per sheet, refill time per room, discarded-material reduction.
- Acceptance criteria: define maximum double-feed rate and minimum guest comfort score before facility-wide rollout.
- Ongoing QC: sample carton inspections, batch color audits, and require pre-shipment photos/videos.
Custom OEM Toilet Paper — Cost-Effective Supply

Can Interfolded Systems Effectively Reduce Consumption by 30%?
Interfolded dispensers can cut visible waste and operating cost; validate with a controlled baseline and 60–90 room-night audits before claiming 30% savings.
Measure and Validate Consumption Reductions: Baseline Metrics and Data Collection
Define baseline metrics up front: sheets per occupied room-night, grams of paper discarded per room, and cost per occupied room. Run weight audits and dispenser counts over a minimum 60–90 room-night period to smooth seasonal variance and capture representative guest behavior; industry case studies as of 2026 report reductions near 30% in comparable luxury properties, but you must prove that on your property.
- Deploy calibrated scales on waste bins and log gram measurements (g) at each audit interval.
- Install inline dispenser counters and maintain housekeeping refill logs to track sheets dispensed and refills per room-night.
- Target metric: calculate percentage change versus baseline; compare matched occupancy profiles (same room types, length of stay, and day-of-week mix).
- Validation protocol: collect pre/post data over identical occupancy profiles and run simple before/after comparisons to isolate dispenser effect from housekeeping policy changes.
Match Interfolded Tissue Specifications to Luxury Standards and Plumbing Requirements
Specify material and performance to avoid guest complaints and plumbing risks: prefer 100% Virgin Wood Pulp or selected Bamboo pulp, insist on OBA-free formulations, and require rapid disintegration for septic safety. Set per-ply GSM targets at 13–22 g/m² and design total GSM to meet softness and wet-strength needs—expect total GSM between roughly 26–66 g/m² depending on ply count.
- Ply and GSM: offer 2–5 ply options; specify per-ply GSM and a target total GSM to balance feel and durability.
- Absorbency & finish: require CNC point-to-point embossing to raise absorbency by ~30% while preserving tactile softness.
- Dimensional fit: confirm folded-sheet dimensions and dispenser throat width; support standard widths 102–132 mm or accept custom folds to prevent jams and misfeeds.
- Compliance checklist: ISO 9001, FDA and EU hygiene alignment, septic-safe performance, and batch-verified brightness 85–92%.
Operational Deployment: Dispenser Selection, Housekeeping Protocols, and ROI Modeling
Select one-at-a-time dispensers built for your folded-sheet dimensions—locked stainless steel or ABS housings for luxury public areas and secure ABS for back-of-house. Map dispenser locations per guest room and public restroom, set mounting positions to avoid reach conflicts, and size units for refill pack counts to minimise service interruptions.
Redefine housekeeping workflows: switch from mandatory roll replacement to a refill-frequency policy, train staff to record refill counts and tamper checks, and log dispenser faults (jams, misfeeds, guest feedback). Model ROI using dispenser capex, maintenance, expected paper savings percentage, and freight efficiencies—use 40HQ payload assumptions of 7–9 tons for sourcing at scale. For procurement, require MOQ 1x40HQ for private label; expect in-stock lead times 10–15 days and production 20–25 days, plus pre-shipment visual verification and batch color consistency.
- ROI inputs: include dispenser capex, routine maintenance cost, projected paper savings (test-derived), and freight assumptions based on 40HQ payload 7–9 tons.
- Procurement: set MOQ = 1 x 40HQ for private label; require pre-shipment photos/videos and batch color checks before final payment.
- Troubleshooting: log faults and corrective actions—adjust dispenser feed tension, swap to a softer ply spec, or change embossing pattern to stop jams or guest complaints.
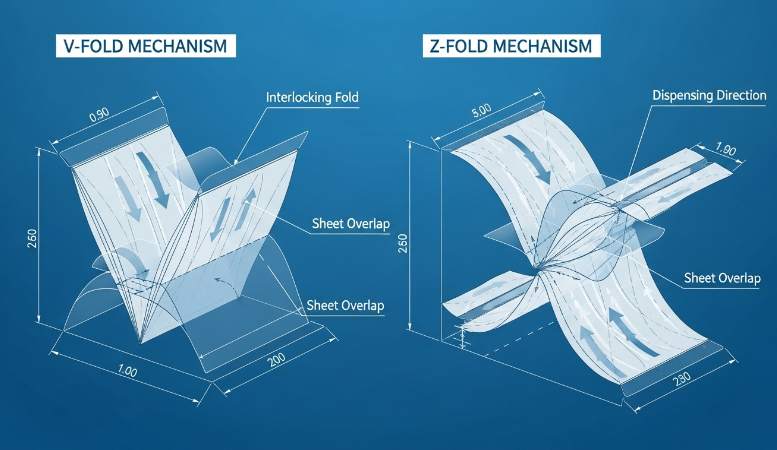
Structural Engineering: The V-Fold vs. Z-Fold Comparison
Selecting the correct fold type directly affects dispenser reliability, guest experience, and total cost of ownership in luxury and high‑traffic facilities.
Material and sheet specifications for V‑Fold vs Z‑Fold
Specify 100% Virgin Wood Pulp as the default for hotel-grade interfolded tissue to secure long-fiber strength and the soft hand guests expect. Control individual-ply density between 13–22 g/m² to strike the balance between tactile softness and wet strength; design targets should hit natural brightness of 85–92% and exclude OBAs to protect sensitive skin. For absorbency, document point-to-point embossing as a formal performance lever—CNC precision emboss patterns have been shown to raise absorbency by roughly 30% and should be defined in the spec sheet.
Match sheet dimensions to dispenser apertures: design sheet widths within 102–132 mm. Require rapid disintegration performance that meets North American and European septic standards for any product intended for those markets. For V‑Fold applications use a simpler center/half fold for compact stacks; for Z‑Fold specify tighter fold geometry to maintain the interlocking zigzag that supports reliable pop‑up dispensing.
- Base fiber: 100% Virgin Wood Pulp (hotel-grade standard)
- Ply density: 13–22 g/m² per ply
- Brightness: 85–92%; OBA‑free
- Absorbency: point‑to‑point embossing → ~30% increase (specify emboss pattern)
- Sheet width constraint: 102–132 mm to match Top Source dispenser apertures
- Septic/plumbing: rapid disintegration compliant with NA and EU standards
Dispensing performance and operational metrics: waste, cost per use, and user flow
Use one‑at‑a‑time interfold designs (Z‑Fold or interfolded pop‑up) to reduce over‑pull and surface contact versus roll systems; operators and case studies report meaningful consumption reductions, but independent literature does not universally confirm a fixed 30% saving, so treat any single figure as site‑specific. Measure performance with a cost‑per‑use metric: record sheets per guest × sheet area (or sheet GSM) and convert to cost per square metre to compare formats fairly. Target consumption reductions that offset dispenser CAPEX over the chosen payback period.
Quantify hygiene gains by counting touchpoints per use and tracking service interval changes—interfolded dispensers reduce surface contact and extend time between staff interventions. Align packaging and pack counts to operational roles: use individually wrapped Format A for guest rooms and bulk bundles Format B for housekeeping to minimize contamination risk while optimizing logistics.
- Single‑sheet retrieval: reduces guest/housekeeping waste relative to rolls
- Cost‑per‑use calculation: sheets per guest × sheet GSM → convert to cost per area for apples‑to‑apples comparison
- Hygiene impact: track touchpoints per use and reduced service intervals as KPIs
- Packaging: Format A (individual wrap) for rooms; Format B (direct bundle) for back‑of‑house
- Recommended luxury model alignment: TSH‑4010 for hotel‑grade interfold deployment
- Sustainability tradeoff: Virgin Wood Pulp for premium feel; Bamboo/Recycled pulp for eco programs (expect differences in softness and absorbency)
Dispenser integration, refill protocol and supply chain controls
Specify fold geometry and sheet overlap so V‑Fold or Z‑Fold stacks feed cleanly through targeted dispenser models. For Z‑Fold require consistent interlock spacing to ensure the pop‑up action; for V‑Fold allow slightly looser stack tolerances but validate feed reliability in the specific dispenser. Define refill protocol: set single‑item refill cadence, assign staff SOPs to replace only empty modules, and train teams to avoid roll‑replacement habits that create waste in luxury properties.
Control supply chain with clear logistics parameters and QC gates: set MOQ at 1×40HQ for private‑label and custom runs; use in‑stock dispatch windows of 10–15 days and production lead times of 20–25 days. Require ISO 9001 plus FDA and EU hygiene compliance, enforce pre‑shipment visual verification and batch color consistency, and size container loads to maximize the 40HQ payload (7–9 tons) while matching refill frequency to housekeeping workflows.
- Mechanical fit checklist: confirm fold type, sheet overlap, aperture clearance, and first‑sheet pop height in dispenser prototype
- Refill SOP: replace only empty packs, log dispenser serial, record date/time, and rotate stock FIFO
- Packaging selection: Format A for guest-facing rooms; Format B for bulk housekeeping supply
- Logistics: MOQ = 1×40HQ; in‑stock dispatch 10–15 days; production 20–25 days
- Quality controls: require ISO 9001, FDA & EU hygiene compliance, pre‑shipment photos/videos, batch color consistency
- Inventory planning: pack to maximize 40HQ payload (7–9 tons) and align container frequency with housekeeping refill cadence
Is the Unit Cost of Interfolded Sheets Justified by Labor Savings?
Compare effective unit cost per usable sheet to measured labor minutes saved; a short pilot will reveal whether dispenser CAPEX pays back.
Calculate sheet-level economics: unit cost, usable sheets and break-even formula
Compute the baseline unit cost per usable sheet with a simple formula: unit cost per usable sheet = total pack cost ÷ usable sheets per pack. Adjust usable sheets for dispenser retention, interfold overlap and real-world yield loss. Then add a labor component to get effective cost per use: effective cost per use = unit cost per sheet + (time_per_change × wage_rate ÷ expected_uses_per_change). Use observed values for time_per_change and expected_uses_per_change rather than manufacturer claims.
Collect these variables before you model ROI: pack cost (FOB), sheets per pack, sheet width (102–132 mm), ply and GSM (13–22 g/m² per ply), dispenser yield loss percentage, time per change, wage rate, and expected uses per change. Factor a baseline waste multiplier (industry reports cite roughly 50% waste from mandatory roll replacement) to compare theoretical consumption to actual use. Note the literature does not reliably prove a fixed 30% consumption reduction; treat any percent savings as an empirical input you must validate in-field. Run a 30-day pilot in 10 rooms, measure sheets dispensed and roll changes avoided, then feed measured values into the formulas and apply this decision rule: deploy interfolded if monthly labor savings + material savings > monthly amortized dispenser CAPEX.
- Pack cost (FOB) and sheets per pack
- Sheet dimensions: width 102–132 mm; ply and GSM 13–22 g/m² per ply
- Dispenser yield loss % and overlap factor
- Time_per_change, wage_rate, expected_uses_per_change
- Baseline waste multiplier (start with 50%)
Quantify housekeeping time and material savings: measurement steps and conversion to cost
Start with direct observation: record average roll-change frequency per room per stay and time per change during housekeeping shifts. Convert observed roll changes avoided into labor minutes saved with this metric: monthly labor minutes saved = (roll_changes_avoided_per_room_per_month × time_per_change) × number_of_rooms. Translate minutes to cost: monthly labor savings = (monthly labor minutes saved ÷ 60) × average_hourly_wage_including_benefits. Use actual payroll loaded rates, not base wages.
Convert material changes to currency by calculating sheets avoided: sheets_avoided = baseline_sheets_used × waste_multiplier − measured_interfolded_sheets_used, then multiply by unit cost per sheet. Account for hygiene-driven shrinkage and theft by applying a containment factor when you reconcile physical inventory. Validate reductions using room-level log sheets, dispenser counters or weight-based inventory checks over a 60–90 day window to avoid seasonal noise; use the validated averages in your ROI model.
- Observe and record roll-change frequency and time per change across shifts
- Calculate monthly labor minutes saved and convert to cost with loaded wage rates
- Compute sheets avoided and convert to currency using unit cost per sheet
- Apply a containment factor for theft/over-pull when reconciling inventory
- Validate with dispenser counters or weight checks over 60–90 days
Procurement and deployment specs: dispenser CAPEX, product match and logistics for ROI
Amortize dispenser CAPEX per room using this formula: monthly amortized cost per room = dispenser_cost_per_unit ÷ amortization_months + installation_costs ÷ total_rooms_served. Size procurement to product spec: select hotel-grade interfolded tissue made from 100% Virgin Wood Pulp, OBA-free, septic-safe, with ply options that match your brand standard (2–5 ply, 13–22 g/m² per ply). For luxury properties prefer Top Source models such as TSH-4010 or custom interfold products with CNC embossing to preserve absorbency and guest feel (CNC embossing can raise absorbency by ~30%).
Optimize logistics: consolidate interfold orders with other tissue SKUs to fill a 40HQ (payload 7–9 tons) and reduce landed cost; expect production lead times of 20–25 days for custom runs. Enforce contract quality checkpoints: require ISO 9001, FDA or EU hygiene compliance, OBA-free certificate, brightness 85–92%, and batch color consistency. Deploy with an SOP pack for housekeeping, install dispensers, and schedule a 3-month review to recalculate ROI using measured labor and material savings.
- CAPEX amortization formula and install cost allocation
- Product spec: 100% Virgin Wood Pulp, OBA-free, septic-safe, ply 2–5, GSM 13–22 g/m²
- Preferred models: TSH-4010 for luxury; consider CNC embossing for +30% absorbency
- Logistics: consolidate SKUs for 40HQ payload (7–9 tons); lead time 20–25 days
- Quality and compliance: ISO 9001, FDA/EU hygiene, OBA-free, brightness 85–92%, batch color consistency
- Deployment actions: procure dispensers, produce housekeeping SOPs, run 3-month ROI review

Dispenser Esthetics: Sleek Designs for Modern Facility Branding
Design dispensers to match paper geometry, finish, and service flow so facilities cut waste, simplify maintenance, and protect brand appearance.
Match dispenser feed and aperture to paper format (roll, coreless/solid roll, interfolded)
Specify dispenser apertures by targeted roll widths: standard commercial widths sit between 102–132 mm, premium comfort models use 165 mm, and oversized systems require 235 mm. Confirm each dispenser accepts bundle weights from small 780 g packs up to 5,000 g mass bundles common with coreless/solid formats (for example, 5,000 g/28-roll variants). Check spindle and tray geometry for coreless support or interfolded feed; run samples from TSH-3396, TSH-4010, TSH-JRT08 and TSH-2559 to verify seating and axial clearance.
Match sheet handling to ply and fiber specs: design feeds for 2–5 ply products where each ply measures about 13–22 g/m² to avoid overfeed or nip jams. Validate perforation and point-to-point embossing compatibility—embossing can lift absorbency by ~30%—and set feed tension low enough to prevent tearing but high enough to secure the next sheet. Field test each dispenser by running 50 dispensing cycles per unit with the target SKU to confirm smooth tear, maximum sheet pull limits, and refill ergonomics before wide rollout.
- Specify aperture widths: 102–132 mm (standard), 165 mm (premium), 235 mm (oversize).
- Confirm capacity for bundle weights 780 g → 5,000 g; validate with 5,000 g/28-roll coreless samples.
- Test spindle/tray geometry with TSH SKUs: TSH-3396, TSH-4010, TSH-JRT08, TSH-2559.
- Design feed for ply density 13–22 g/m² per ply and 2–5 ply products to reduce jams.
- Adjust feed tension for perforation and point-to-point embossing (absorbency +~30%).
- Run 50-cycle field test per unit; record tear quality, max pull, and refill ergonomics.
Surface, finish, and marking specs for brand-consistent dispensers
Select housing materials that balance aesthetic and durability: use 304 stainless steel in brushed or polished finishes for high-end zones, or ABS thermoplastic with a UV-stable powder coat for color-matched installations. Favor matte or brushed surfaces to reduce fingerprints and specify chemical-resistance to common disinfectants used by housekeeping so finish integrity survives regular cleaning cycles.
Define logo placement and production method up front: allocate a front-center panel band 40–80 mm wide and specify laser etching or UV-cured printing for abrasion resistance. Lock color tolerances for plastic housings and printed panels to maintain batch color consistency across sites. Add tamper-proof hardware and choose a service access method—keyed lock or quick-release—so technicians access internals without compromising clean lines.
- Housing options: 304 stainless steel (brushed/polished) or ABS thermoplastic with UV-stable powder coat.
- Finish spec: matte/brushed to reduce fingerprints; require resistance to standard disinfectants.
- Logo area: front-center band 40–80 mm; use laser etch or UV-cured print for abrasion resistance.
- Enforce batch color consistency for plastic housings and printed panels across containers.
- Security and service: specify tamper-proof hardware and keyed lock or quick-release access.
Installation and operational workflow to minimize waste and reinforce sustainability messaging
Pilot interfolded one-at-a-time dispensers in luxury restrooms to cut paper waste and reduce mandatory roll replacements; run pilots in 5–10 rooms and measure paper consumption per guest against baseline. Pair dispenser type to product strategy: choose interfolded or individually wrapped rolls for hospitality (TSH-4010) and select coreless solid rolls (TSH-3396, TSH-3082) for high-turnover, cost-sensitive locations to maximize usable paper per kilogram.
Standardize refill and housekeeping procedures: set refill intervals, require staff to log remaining paper at check-out, and train teams to promote single-sheet dispensing to avoid discarding partially used packs. Track operational KPIs—paper consumption per guest, refill frequency, and projected payback period for dispenser investment—and require measurable waste reduction before scaling. Use product claims in guest communications where relevant: highlight 100% Virgin Wood Pulp, OBA-free composition, or septic-safe attributes to align sustainability with brand positioning.
- Pilot: install interfolded dispensers in 5–10 rooms; measure consumption change vs baseline.
- Product pairing: TSH-4010 for hospitality interfolded/individually wrapped; TSH-3396 / TSH-3082 for coreless high-turnover sites.
- Refill protocol: standardize intervals, log remaining stock at check-out, train staff on one-sheet dispensing.
- KPIs to track: paper consumption per guest, refill frequency, dispenser payback period.
- Communications: highlight 100% Virgin Wood Pulp, OBA-free, and septic-safe claims on signage or digital guest materials where sustainability matters.
Conclusion
Proper installation and wiring reduce safety risks, keep fixtures aligned with OSHA rules, and prevent costly failures. Completing work to code also extends equipment life and lowers long-term maintenance needs.
Start by reviewing your property’s current fixtures and maintenance records to identify gaps. Contact our team to request a certified lighting catalog and a sample pack for on-site evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is interfolded toilet tissue and how does it work?
Interfolded (pop-up) toilet tissue is supplied as interleaved single sheets in a dispenser so that pulling one sheet presents the next; the one-at-a-time dispensing mechanism prevents over-pulling and enables more contactless access.
Does interfolded tissue really reduce paper waste in restrooms?
Yes; research from luxury hotels shows mandatory roll-replacement policies can waste roughly half of purchased paper, and switching to one-at-a-time interfolded dispensers limits consumption because users can only pull single sheets, leading to reported reductions in material use and lower long‑term costs.
Why do hospitals prefer pop-up tissue over standard rolls?
The research highlights hygiene as a key benefit: pop-up interfolded dispensers minimize cross-contamination by allowing users to take a sheet without touching dispenser surfaces, so the contactless one-at-a-time access supports infection‑control priorities in clinical and shared-restroom settings.
Are interfolded tissue dispensers compatible with bulk-buy sheets?
Generally no; interfolded dispensers are designed for interleaved stacks of single sheets rather than bulk roll or continuous-sheet formats, so compatibility depends on the dispenser design and most bulk roll products will not fit interfolded dispensers.
What is the difference between V-fold and Z-fold tissue?
The provided research does not compare V-fold and Z-fold designs; it focuses on the operational benefits of interfolded/pop-up systems such as waste reduction, sustainability, and hygiene rather than specific fold patterns—consult manufacturer specifications for fold-type differences.
How to calculate the cost-per-user for interfolded vs. rolls?
The research does not provide a numeric formula, but it explains that reduced consumption from one-at-a-time dispensing typically lowers cost-per-user over time as material savings offset the initial dispenser investment; a practical calculation is to total tissue spend plus the amortized dispenser cost for a chosen period, then divide by the number of users in that period, and compare that to the same calculation for roll-based supply.



