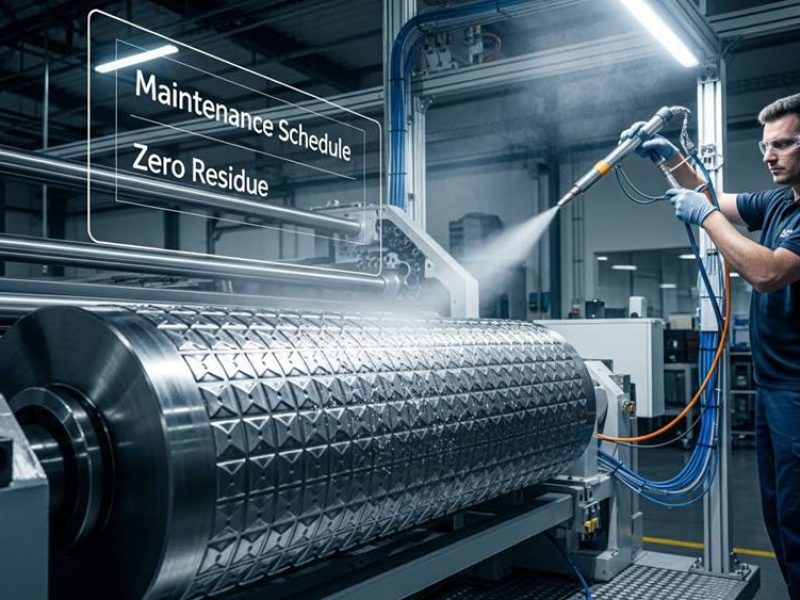
Achieving a ‘clean label’ for premium hygiene products requires balancing structural integrity with high-bulk targets exceeding 15 cc/g. While mechanical edge-embossing eliminates chemical adhesives, process instability often leads to a 27% reduction in shear strength when PDMS-based contaminants interfere with fiber entanglement. Engineering the perfect bond requires precise control over localized compression, where stress peaks can reach 70 MPa at the nip point, making the difference between product failure and a high-retention finish.
This technical report evaluates the mechanical parameters defined by ISO 12625-1:2019 and ISO 13444 knurling geometries to ensure ply-bonding without introducing tactile stiffness. We examine the impact of 3.2 bar nip pressure on volumetric expansion and detail the FDA Class II regulatory framework necessary for achieving biocompatible, residue-free tissue applications for sensitive skin.
The Role of Edge-Embossing in Multi-Ply Tissue
Edge-embossing uses mechanical patterns along paper edges to secure plies without adhesives, maintaining high central bulk exceeding 15 cc/g according to ISO 12625-1:2019 standards.
Mechanical Ply Bonding and ISO 12625-1:2019 Standards
Mechanical ply bonding relies on localized compression to lock layers together. This technique follows ISO 12625-1:2019 (3.22.2), which identifies edge-embossing as small, continuous traces applied only to the web periphery. By concentrating the bond on the edges, manufacturers eliminate the need for heavy chemical adhesives, protecting the “clean label” status of premium hygiene products.
The bonding process works through single or multi-nip embossing stations that handle 2-ply to 5-ply structures. Engineers integrate specific pattern geometries to ensure the plies remain connected during consumer use while keeping the center of the sheet soft and airy.
- Pattern Density: 5-15 nested dots per cm² on the secondary ply.
- Geometry: Curvilinear line elements that house nested dot patterns for mechanical attachment.
- Standard Classification: ISO 3.22.2 compliant “endless traces” distinct from full-sheet embossing.
Technical Parameters for High-Bulk Product Integrity
Maintaining product integrity at high speeds requires strict adherence to technical tolerances. Modern converting lines must achieve high bulk—specifically greater than 15 cc/g—while processing sheets with basis weights between 20 and 60 gsm. The goal is to balance tensile strength with nesting efficiency.
- Surface Coverage: 10-30% on the first ply; 5-10% preferred dot coverage on the second ply.
- Element Dimensions: Wave-like segments measuring 30-60 mm in length.
- MD Alignment: Elements set at 5-15° (optimally 8°) relative to the Machine Direction.
- Operational Speed: 120-150 m/min for edge-specific pattern application using steel-to-rubber or steel-to-steel nips.
Production stability depends on Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) systems. These setups outperform traditional gear systems by achieving 98-99.5% pattern pass rates and reducing waste to less than 5 meters per changeover. This precision ensures uniform depth during the marrying roll process, where dots partially nest into line elements to create the final bond without deforming the base sheet.

Mechanical vs. Adhesive Bonding: The Softness Trade-off
Mechanical interlocking preserves bulk through physical friction, while adhesive bonding lowers stress peaks but risks tactile stiffness if bondlines exceed 0.3 mm.
| Metric | Mechanical Bonding | Adhesive Bonding |
|---|---|---|
| Stress Distribution | Localized (Up to 70 MPa) | Uniform (Reduced to 9–35 MPa) |
| Optimal Thickness | Surface Topography Dependent | 0.2 mm – 0.3 mm |
| Product Bulk | High Retention (>15 cc/g) | Potential for Stiffness/Plasticity |
| Common Failure Load | Friction-limited | 40-46% higher with proper nips |
Physical Interlocking and Surface Topography in Mechanical Bonding
Mechanical bonding avoids chemical binders to maintain the high-bulk targets required for premium multi-ply tissue. This method relies on surface roughness and physical fiber entanglement. Shear strength in these joints scales directly with the complexity of the substrate topography. High-viscosity agents penetrate these rough surfaces more effectively than low-viscosity alternatives, creating convoluted failure paths that resist separation.
- Fracture Energy: Reaches 4.5 N/mm in standard DCB tests.
- Contaminant Sensitivity: PDMS-based contaminants like Frekote reduce shear strength by 27%.
- Target Bulk: Designed for products exceeding 15 cc/g sheet bulk.
- Eco-Label Benefits: Minimizes added stiffness, making it the preferred choice for “clean label” brands.
Stress Peak Mitigation and the Softness-Bondline Correlation
Adhesives offer superior joint uniformity by spreading mechanical loads across a wider area. While spot-style mechanical welds concentrate stress at 70 MPa, bead applications or extended bondlines drop those peaks to 9–35 MPa. Tactile softness depends on the bondline thickness; exceeding the 0.45 mm threshold introduces excessive plasticity and lowers the overall joint failure load.
- Optimal Bondline: 0.2–0.3 mm (often maintained using glass bead spacers).
- Adhesive Type: Rigid options like SikaPower® concentrate stress; flexible alternatives suit pliable paperboard.
- Overlap Geometry: Minimum 10 mm length is required for thin sheets to prevent strength decay.
- Production Speed: Effective bonding is maintained at machine speeds of 120–230 m/min.
Engineering standards emphasize MPa-based characterization where the width-to-length ratio of the overlap dictates real-world performance. For multi-ply tissue, nesting dot patterns into curvilinear line elements provides the mechanical grip needed to avoid the 27% strength loss caused by surface contaminants while maintaining the hand-feel consumers expect.
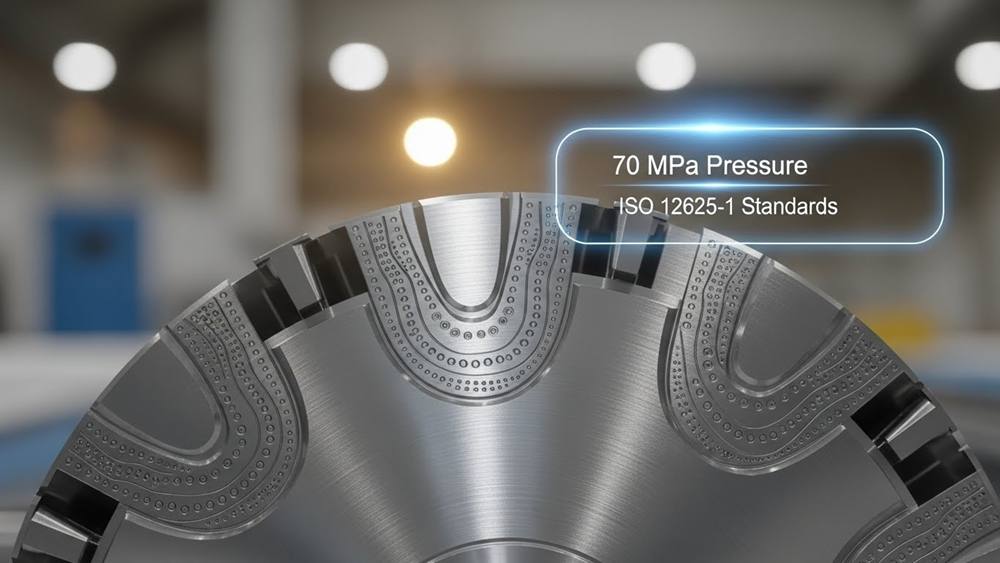
Designing the Knurling Pattern for Structural Integrity
Structural integrity requires ISO 13444 standards and 90° profile angles. Apply precise pre-knurl formulas like d1-0.5p to control material displacement and prevent fatigue-related micro-cracks.
| Parameter | Value / Formula | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Profile Angle | 90° | Standardized uniformity |
| Pre-Knurl (Type A) | d = d1 – 0.5p | Straight patterns |
| Pre-Knurl (Type B) | d = d1 – 0.67p | Diamond patterns |
| Tooth Depth | 0.2 – 0.5 mm | Penetration target |
| Diameter Growth | 0.5 – 1.5 mm | Post-process tolerance |
Standardized Knurling Geometries: ISO 13444 Type A and Type B Patterns
ISO 13444:2012 defines the geometric boundaries for patterns that provide mechanical grip without compromising the base material. Engineers must select between two primary configurations to ensure predictable surface deformation and avoid part failure.
- Type A: Straight teeth running parallel to the axis or at a 30° helix.
- Type B: Diamond patterns engineered for high-torque applications.
- Profile Angle: A strict 90° angle maintains uniformity and prevents stress concentrations.
Type B patterns create greater radial displacement. This makes them effective for high-torque needs, but they require careful management to prevent thin-wall collapse in hollow components.
Technical Parameters and Displacement Formulas for Precision Engineering
Calculated material growth is the difference between a functional part and scrap. The diametral pitch (p) must scale with the component size to maintain structural integrity. Small diameters (2-4 mm) typically utilize a 0.8 mm pitch, while industrial components exceeding 60 mm require up to a 1.6 mm pitch.
Precision diameter formulas control how much material migrates during the process. Using the wrong formula for a diamond pattern often results in diameter overages or material cracking.
- Straight Knurling: Use d = d1 – 0.5p to determine pre-knurl diameter.
- Diamond Knurling: Use d = d1 – 0.67p to account for increased radial flow.
- Tolerances: Design specifications should follow ANSI/ASME B94.6 or DIN 82 standards.
- Helical Angles: Diamond and diagonal patterns generally use 30° or 45° angles.
Engineers prioritize ductility for form knurling. If the material is too brittle or the displacement is not calculated correctly, the process introduces micro-cracks that lead to fatigue failure under mechanical load. Using internal mandrels for hollow parts helps maintain dimensional accuracy during these high-pressure deformations.
Scale Your Brand with 30 Years of Expert OEM Toilet Paper Manufacturing

Minimizing Glue Residue for Sensitive Skin Applications
Adherence to ISO 10993 and FDA Class II controls ensures biocompatibility. Optimize silicone gel thickness to 80-150 microns and limit skin stripping to 20% to prevent irritation and pain.
Biocompatibility Standards and Regulatory Compliance
Manufacturers must follow strict safety frameworks to prevent chemical burns, inflammation, or allergic reactions. FDA Class II special controls under 21 CFR 878.4010 require specific risk mitigation for fumes and unintended bonding. Engineering validation relies on mechanical testing to ensure the polymerized bond holds without manual support.
- ISO 10993-10: Testing for sensitization and skin irritation.
- ISO 10993-5: Cytotoxicity testing to protect mammalian cells.
- ISO 10993-1:2003: Standards for prolonged skin contact (24 hours to 30 days).
- 21 CFR 878.4010: FDA compliance for topical skin approximation and residue control.
Adhering to these standards ensures the adhesive performs safely on breached skin or sensitive surfaces. Animal studies and histopathology reports often validate these metrics to confirm no delayed healing occurs due to adhesive interference.
Technical Metrics for Residue-Free Removal
Precision in adhesive application prevents the “edge lift” that leads to residue buildup. For silicone gel adhesives, maintaining a specific thickness provides enough tack for bonding without fusing to the epidermal layer. This balance is critical for “clean label” products that prioritize hypoallergenic performance.
- Adhesive Thickness: 80 to 150 microns.
- Stripping Effect: Maximum 20% removal of the epidermal layer.
- Pain Threshold: Average score below 2.5 on the Wong-Baker scale.
- Surface Prep: Zero use of petroleum jelly or oils before application.
Proper surface preparation is as vital as the adhesive chemistry. Contaminants like moisture, hair, or existing oils prevent uniform polymerization. Avoiding petroleum-based pre-coatings ensures the adhesive lifts cleanly, leaving no sticky traces or chemical runoff that could irritate the eyes or mucosal membranes.

Impact of Embossing Pressure on Perceived Bulkiness
Increasing pressure from 0 to 3.2 bar doubles tissue bulk. Peak performance at 2.8 bar maximizes volume without compromising fiber integrity or tensile strength.
Correlation Between Nip Pressure and Volumetric Expansion
Increasing nip pressure forces paper fibers into the roll topography, expanding the vertical profile of the sheet. This mechanical deformation creates the loft and air pockets necessary for premium tissue grades.
- Bulk Volume: Increases from ~6.5 cm³/g to over 16.1 cm³/g at 3.2 bar pressure.
- Sheet Thickness: Expands from a base of 0.102 mm to 0.270 mm at peak settings.
- Apparent Porosity: Rises from 89.2% to 95.6%, creating the “clean label” loft required for high-end softness.
These air pockets are the primary driver of perceived softness. While the physical weight remains constant, the increased volume changes the consumer’s tactile perception of the product.
Technical Thresholds and Structural Integrity Standards
Structural limits dictate the ceiling for pressure application. While higher pressure adds bulk, it simultaneously stresses fiber bonds. Engineers must balance these forces to prevent the web from becoming brittle.
- Tensile Peak: Optimization occurs at 2.8 bar; exceeding this risks fiber bond breakage.
- Industrial Nip Range: High-pressure systems operate between 1,000 and 3,000 psi.
- Roll Hardness: Use <40 P&J for anvils and >40 P&J for embossing wheels.
- Quality Standards: Adherence to ISO 12625-3 (bulk) and ISO 12625-4 (tensile) ensures consistency.
Finite element analysis (FEA) modeling simulates MD/CD plastic strain to prevent edge bulk flow during high-speed production. Also, precision testing via Thwing-Albert VantageNX systems confirms that the material meets tensile requirements after the embossing process.
Maintenance of Steel-to-Steel Embossing Wheels
Preventive cleaning and air knife calibration stop vibrations that trigger 3-5 month lead times for steel roll replacements. Surface integrity and moisture control are mandatory.
Surface Preservation and Preventive Inspection Schedules
Daily maintenance protects the surface roughness required for ply bonding. If you ignore debris buildup, the resulting vibration destroys the engraving, forcing a 3-5 month production halt for roll replacement.
- Daily Cleaning: Use pickling, organic degreasing, or mechanical blasting to maintain surface roughness and bonding efficiency.
- Lubrication: Apply white oil consistently to the engraved surface and verify the rotating brush roll functionality.
- Corrosion Control: Keep rolls dry in humid environments to prevent rust; moisture is the primary enemy of steel roll longevity.
- Debris Removal: Schedule periodic stops to remove deposits that cause mechanical vibrations.
Precision Cleaning Methodologies and Mechanical Calibration
Manual cleaning creates inconsistent wear and safety hazards. Use air knife nozzles with compressed air or solvents to strip debris without surface contact. Calibration must match the specific roll width to ensure uniform pressure.
- Air Knife Position: Fix nozzles exactly 6-8 inches from the roll surface with slit openings calibrated to match roll width.
- Pressure Analysis: Measure nip widths via PLI (pounds per linear inch) impressions to ensure even distribution across the embossing face.
- System Metrics: Monitor bearing lubrication and paired roll durometer; rubber roll recovery takes 4-6 weeks if misaligned.
- Optimization: Verify circumference and roll alignment to maintain pattern definition and tensile strength.
Final Thoughts
Mechanical edge-embossing is the only way to hit 15 cc/g bulk while maintaining a “clean label.” While glue bonding is stronger, it creates tactile stiffness that ruins premium hygiene product positioning.
Calibrate your nip pressure to 2.8 bar and mandate daily air-knife cleaning of steel rolls. This optimizes softness immediately while preventing the vibration damage that triggers catastrophic five-month replacement lead times.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do the layers of some toilet paper separate during use?
Layers separate because manufacturers engineer an intermediate central section of weakly bonded fibers to simulate bulk and softness. These fibers fail under mechanical shear forces during use. Perforations are typically spaced at 5.0–6.5 inch intervals to help maintain the remaining structural integrity.
What is the difference between full embossing and edge embossing?
Full embossing applies patterns across the entire surface using matched steel rollers. Edge embossing limits the pattern to the sealing rim, preserving the central area for print quality and EAN code readability. Total embossing height for edge patterns reaches a maximum of 140µ, often reduced to 126µ in production.
Is mechanical ply-bonding as strong as glue lamination?
No. Glue lamination achieves block-shear bonding strengths up to 3.14 MPa at standard industrial pressures. Mechanical ply-bonding lacks comparable quantified strength ratings and is consistently less durable under stress.
Can I customize the design of the edge-embossing track?
Yes. Manufacturers use electromechanical engraving or laser ablation to create intricate custom patterns. Engraving depths on the steel rolls range from a few microns to several millimeters, allowing for specific brand textures.
Does edge-embossing affect the overall softness of the roll?
Yes. Finishing geometry significantly impacts bulk and hand-feel (HF). Round finishing geometry can double the bulk compared to base paper, but HF values typically decrease as bulk increases in micropatterns.
How to test ply-bonding strength in a factory setting?
Factories use the Scott internal bond test (TAPPI T 569). A specimen is pressed with double-coated tape at 690 kPa (100 psi) and delaminated via a pendulum tester. High-quality multi-ply materials typically score above 600 J/m².
SEO
Title: Edge-Embossing Precision: Achieving Ply-Bonding Without Excessive Glue
Description: Mechanical edge-embossing achieves 15 cc/g bulk without adhesives. Explore ISO standards and technical parameters for premium tissue.
URL: mechanical-edge-embossing
Keywords: Mechanical Edge-Embossing


